No.333,jinyuan fourth road,jiangqiao town,jiading district,Shanghai
Tel:021-39556131
Fex:021-39556131
Email:info@senpu-sh.com
website:www.senpu-sh.com

No.333,jinyuan fourth road,jiangqiao town,jiading district,Shanghai
Tel:021-39556131
Fex:021-39556131
Email:info@senpu-sh.com
website:www.senpu-sh.com
Shanghai Senpu Electric Research Institute, Shanghai Sendi Voltage Regulation and Transformer Equipment Co., Ltd. Zhang Jingzhou Xu Kaiping
1 The difference between a voltage regulator and a voltage regulator
A voltage regulator is a voltage regulation power supply that converts the rated power supply voltage into an output voltage that can be steplessly, smoothly, and continuously adjusted from the minimum to the maximum. A regulator with a nominal minimum voltage of zero, the no-load output allows a lower starting voltage. The rated output voltage of the voltage regulator refers to the specified maximum output voltage after removing the internal impedance voltage drop under the load state.
A voltage regulator is a regulated power supply whose power supply voltage fluctuates within a certain range, and is automatically controlled by a closed loop to stabilize the output voltage within the required accuracy range. The rated output voltage of the voltage stabilizer refers to the specified voltage after removing the internal impedance voltage drop under the load state.
The rated load of the voltage regulator and voltage stabilizer means that the output voltage and output current are both rated values, and the load power factor COSΦ=0.8 (hysteresis).
Different from the voltage regulator and the voltage stabilizer, the rated output voltage of the transformer refers to the specified voltage at the output terminal under no-load state. Since the voltage does not remove the internal impedance voltage drop, the technical data must list the impedance voltage uK value.
The rated output capacity of the voltage regulator and voltage stabilizer is nominally rated capacity, and the formula for calculating the rated capacity is as follows.
![]()
In the formula: m——the number of phases, 1 for single phase and 3 for three phases;
PN——The rated capacity of the voltage regulator and voltage stabilizer, kVA;
U2N——The rated output voltage of the voltage regulator and voltage stabilizer (COSΦ=0.8 lag), V;
I2N——The rated output current of the voltage regulator and voltage stabilizer, A.
If the rated capacity of the voltage regulator and voltage stabilizer has been selected, the rated output current of the voltage regulator and voltage stabilizer can be obtained according to the following formula.
![]()
In any load state, the output current of the voltage regulator and voltage stabilizer cannot exceed the rated value I2N. The output voltage of the voltage regulator is the rated value U2N, so its output power P2 is a constant value PN, and the output voltage of the voltage regulator is adjustable from the minimum value to the maximum value, so its output power P2 is proportional to the output voltage U2. change linearly.
2 Types of voltage regulators and voltage regulators
a. According to the number of phases, there are 1-phase and 3-phase;
b. According to frequency, there are power frequency 50, 60Hz, intermediate frequency 400, 500Hz;
c. According to the cooling method, there are dry self-cooling, oil-immersed self-cooling, and dry air-cooling;
d. According to the voltage level, there are 1kV and below, 6kV, 10kV;
e. According to the structure, there are contact type (with contacts): contact voltage regulator, contact voltage stabilizer, column voltage regulator, column voltage stabilizer;
Induction type (motor type): induction voltage regulator, induction voltage regulator;
Shifting coil type (transformer type): coil shifting voltage regulator;
Magnetic type (DC excitation): magnetic voltage regulator;
Thyristor type (electronic type): thyristor voltage regulator, thyristor power regulator.
Due to the large number of consumables and the large waveform distortion, the voltage stabilizer seldom uses the shifting voltage regulator; the magnetic voltage regulator has large waveform distortion and low power factor at low load, so it is not suitable to make a voltage stabilizer; The waveform is incomplete and the waveform is seriously distorted. The thyristor power regulator will have an impact on the power grid and the load due to the intermittent energization of the load, so the two cannot be made into a voltage stabilizer.
3 The principle of voltage regulator and voltage stabilizer
a. Contact Regulator
Change the contact position of the brush, and change the turns ratio of the primary winding and the secondary winding to achieve the purpose of voltage regulation. A ring-type iron core is called a ring-type contact voltage regulator, abbreviated as a contact voltage regulator.
b. Column Regulator
The principle of voltage regulation is the same as that of the ring-type contact voltage regulator, but the iron core is column-type, so it is called a column-type voltage regulator.
c. Induction regulator
The electromagnetic structure is similar to the locked rotor asynchronous motor. When the relative angular displacement between the stator and the rotor changes continuously, the vector sum of the two potentials changes accordingly, and finally a stepless, smooth and continuously regulated output is obtained. Voltage.
d. Coil shift regulator
By moving the position of a moving coil that is short-circuited by itself, the flux linkage between the primary and secondary coils is changed to obtain a stepless, smooth and continuously regulated output voltage.
e. Magnetic regulator
The saturable reactor and the transformer are combined together, and the magnetic permeability of the core of the reactor is changed by direct current excitation, and then the voltage distribution of the saturable reactor and the transformer coil is improved to obtain the required output voltage.
f. SCR voltage regulator
By changing the conduction angle of the sine wave of the power supply, the effective value of the output voltage can be changed, so that the output voltage can be adjusted steplessly, smoothly and continuously within a certain range.
g. SCR power regulator
In the set period, change the number of cycles of the voltage applied to the load, and the load power changes with the number of cycles passed.
h. Contact voltage stabilizer, column voltage stabilizer, induction voltage stabilizer
It consists of specially designed contact voltage regulators, column voltage regulators, induction voltage regulators, and sometimes a series-connected transformer to form a closed-loop automatic control system with the controller or control cabinet, that is, a set (set) Complete range of contact regulators, column regulators, induction regulators.
4 Use of voltage regulators and voltage stabilizers
All kinds of voltage regulators can adjust the output voltage steplessly, smoothly and continuously under the load state. Contact voltage regulators are mainly used in small-capacity voltage regulation occasions such as laboratories and equipment matching; induction voltage regulators and column voltage regulators are mainly used in electromechanical, metallurgy, chemical, communication, military, electrical and electrical testing and load voltage requirements Adjusting occasions; magnetic voltage regulators are mainly used in non-ferrous metal smelting, electrolysis, electroplating, quartz glass products and chemical raw materials production and other industries; thyristor voltage regulators and power regulators are mainly used in temperature control occasions such as electric heating, while The thyristor voltage regulator can also be used as a dimming power supply for theaters, theaters, stadiums, and squares; the coil-shifting voltage regulator has many consumables and poor performance, and has been rarely produced and used.
Various types of voltage stabilizers can stabilize the output voltage steplessly, smoothly and continuously under load conditions. Voltage stabilizers are mainly used in metallurgy, mining, chemical industry, airports, buildings, hotels, hospitals, stadiums, computer rooms, medical equipment, production lines and other occasions that require stable load voltage.
5 Voltage regulator, voltage regulator selection
5.1 Select voltage regulator and voltage stabilizer according to load voltage and load current
The rated output voltage U2N of the voltage regulator and voltage stabilizer and its variation range should be consistent with the voltage required by the load and its variation range. The rated output current I2N must be equal to or slightly greater than the maximum current required by the load. A chapter formula calculation. Contact voltage regulators and voltage stabilizers can be used for small-capacity products, and induction or column-type voltage regulators and voltage stabilizers can be used for medium and large-capacity products.
If the rated output voltage and rated output current of the voltage regulator and voltage stabilizer exceed the actual value of the load, the equipment investment will be increased. press.
5.2 Select voltage regulators and voltage stabilizers according to performance requirements
Low impedance and small waveform distortion are required, and column-type voltage regulators and voltage stabilizers are to be used. In the case of low voltage and high current or the load is prone to short-circuit, magnetic voltage regulators are to be used; there is no requirement for waveform distortion, and it is only used for temperature control or dimming The thyristor voltage regulator is optional, the thyristor power regulator only supplies power to the load at intervals in the cycle, and it can only be used as a temperature control power supply for electric heating loads.
5.3 Select the voltage regulator and voltage stabilizer according to the usage environment
For occasions with fire protection requirements, dry-type self-cooling or dry-type air-cooled voltage regulators and voltage stabilizers can be selected; for occasions with anti-corrosion requirements, oil-immersed self-cooling voltage regulators and voltage stabilizers should be used; for outdoor The regulator used should also be an oil-immersed self-cooling regulator, and its control system and the main regulator of the regulator should be placed in a well-sealed oil tank with rain and snow protection.
5.4 Select the voltage stabilizer according to the actual fluctuation range of the power supply voltage
The voltage fluctuation range of the rated input voltage of the voltage stabilizer should be consistent with the actual fluctuation range of the power supply voltage. The voltage fluctuation range expressed as a percentage of the rated input voltage generally has three levels:±10%,±15%, and±20%. The positive and negative voltage fluctuation ranges It can also vary, and it is proposed to take two grades of +10-15% and +15-20%. When the material consumption is constant, the rated capacity is inversely proportional to the voltage fluctuation range. For example, when the voltage fluctuation range is changed from±20% to±10%, the rated capacity will be doubled, and the product efficiency will also be significantly improved.
Unrealistically expanding the voltage fluctuation range of the voltage stabilizer will not only reduce the operation efficiency of the voltage stabilizer, but also increase the investment cost of the equipment.
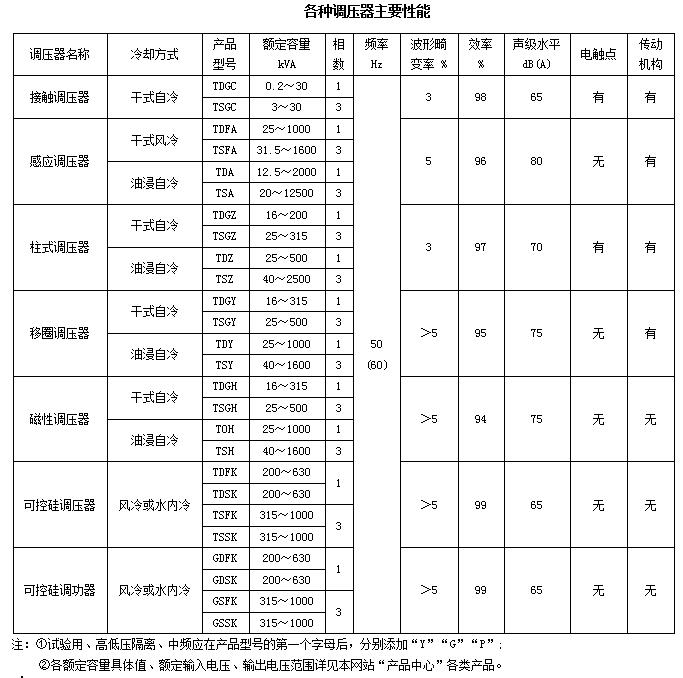
The main performance of various voltage regulators
